POLLUTION AND POLLUTANTS
·
Pollution may be defined as addition of undesirable material into the environment as a result of human activities.
·
The agents which cause environmental
pollution are called pollutants.
·
A pollutants may be defined as a physical, chemical or biological substance
unintentionally released into the environment which is directly or indirectly
harmful to humans and other living organisms.
TYPES OF POLLUTION
Pollution may be of the following types:
·
Air pollution
·
Noise pollution
·
Water pollution
·
Soil pollution
·
Thermal pollution
·
Radiation
pollution
AIR POLLUTION
·
Air pollution is a result of industrial and
certain domestic activity.
·
An ever increasing use of fossil fuels in
power plants, industries, transportation, mining, construction of buildings,
stone quarries had led to air pollution.
·
Air
pollution may be defined as the presence
of any solid, liquid or gaseous substance including noise and radioactive
radiation in the atmosphere in such
concentration that may be directly and indirectly injurious to humans or other
living organisms, plants, property or interferes with the normal environmental
processes.
·
Air pollutants are of two types :
(1)
suspended particulate matter, and
(2)
gaseous pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2), NOx etc.
Particulate pollutants :
·
Particulate matter suspended
in air are dust and soot released from the industrial chimneys.
·
Their size ranges
from 0.001 to 500 μm in diameter.
·
Particles less
than 10μm float and move freely with the air current.
·
Particles which are more than 10μm in
diameter settle down.
·
Particles less
than 0.02 μm form persisent aerosols.
·
Major source of SPM
(suspended particulate matter) are vehicles, power plants, construction
activities, oil refinery, railway yard, market place, industries, etc.
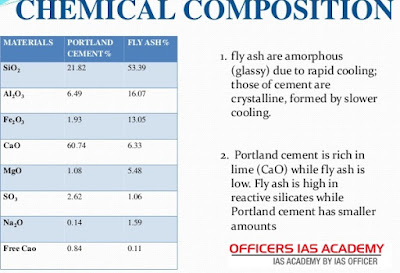
Fly ash : (2015 prelims)
·
Fly ash is ejected mostly
by thermal power plants as by products of coal burning operations.
·
Fly ash pollutes air and water and may cause heavy metal pollution in water bodies.
·
Fly ash affects vegetation as a result of its
direct deposition on leaf surfaces or indirectly through its deposition on
soil.
·
Fly ash is now
being used for making bricks and as a land fill material.
Lead and other metals particles
:
·
Tetraethyl lead (TEL) is used
as an anti-knock agent in petrol for
smooth and easy running of vehicles.
·
The lead particles coming out from the
exhaust pipes of vehicles is mixed with air.
·
If inhaled it produces injurious effects on kidney and liver and interferes with
development of red blood cells.
·
Lead mixed with water and food can create
cumulative poisoning.
·
It has long term effects
on children as it lowers intelligence.
·
Oxides of iron, aluminum, manganese,
magnesium, zinc and other metals have adverse effect due to deposition of dust
on plants during mining operations and metallurgical processes.
·
They create physiological, biochemical and
developmental disorders in plants
and also contribute towards
reproductive failure in plants.
Gaseous pollutants :
Power plants, industries, different types of
vehicles – both private and commercial use
petrol, diesel as fuel and release gaseous pollutants such as carbon dioxide, oxides of
nitrogen and sulphur dioxide along with
particulate matter in the form of smoke.
All of these have harmful effects on plants
and humans.
Table lists some of these pollutants, their
sources and harmful effects.
Gaseous air pollutants: their sources and effects :
|
Pollutant
|
Source
|
Harmful effect
|
|
Carbon compound
(CO and CO2)
|
Automobile exhaust
burning of wood and coal
|
· Respiratory problems
· Green house effect
|
|
Sulphur compounds (SO2 and H2S)
|
Power plants and refineries
volcanic eruptions
|
· Respiratory problems in humans
· Loss of chlorophyll in plants (chlorosis)
·
Acid rain
|
|
Nitrogen Compound (NO and N2O)
|
Motor vehicle exhaust
atmospheric reaction
|
·
Irritation in eyes
and lungs
·
Low productivity
in plants
·
Acid rain damages
material (metals and stone)
|
|
Hydrocarbons (benzene, ethylene)
|
Automobiles and petroleum industries
|
·
Respiratory
problem
·
Cancer causing
properties
|
|
SPM (Suspended
Particulate Matter) (Any soild and liquid)
particles suspended in the air, (flush, dust, lead)
|
Thermal power plants,
Construction activities,
metalurgical processes and automobiles
|
·
Poor visibility,
breathing problems
·
Lead interfers
with the development of red blood diseases and cancer.
·
Smoge (skoke &
fog) formation leads to poor visibility and aggravates asthma in patients
|
|
Fibres (Cotton, wool)
|
Textiles and carpet weaving industries
|
·
Lung disorders
|
|
|
|
|
Prevention and control of air
pollution
(i) Indoor air pollution :
·
Poor ventilation due to faulty design of buildings leads to pollution of the
confined space.
·
Paints, carpets, furniture, etc. in rooms may
give out volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
·
Use of disinfectants, fumigants, etc. may
release hazardous gases.
·
In hospitals, pathogens present in waste
remain in the air in the form of spores.
·
This can result in hospital acquired
infections and is an occupational health hazard.
·
In congested areas, slums and rural areas
burning of firewood and biomass results in lot of smoke.
·
Children and ladies exposed to smoke may
suffer from acute respiratory problems which include running nose, cough, sore
throat, lung infection, asthama, difficulty in breathing, noisy respiration and
wheezing.
(ii) Prevention and control of
indoor air pollution :
·
Use of wood and dung cakes should be replaced
by cleaner fuels such as biogas, limited kerosene or limited electricity.
·
The house designs should incorporate a well
ventilated kitchen.
·
Use of biogas and CNG
(Compressed Natural Gas) need to be encouraged.
·
Those species of trees such as baval (Acacia nilotica) which
are least smoky should be planted and used.
·
Charcoal is a comparatively
cleaner fuel.
(iii) Prevention and control of
industrial pollution
Industrial pollution can be greatly reduced
by:
·
use of cleaner fuels such as liquefied
natural gas (LNG) in power plants, fertilizer
plants etc. which is cheaper in addition to being environmentally friendly.
·
installing devices which reduce release of
pollutants.
·
Devices like filters, electrostatic precipitators,
inertial collectors, scrubbers, gravel bed filters or dry scrubbers are described
below:
(i) Filters :
·
Filters remove particulate matter from the
gas stream.
·
The medium of a filter may be made of fibrous materials like cloth, granular material
like sand, a rigid material like screen, or any mat like felt pad.
·
Baghouse filtration system is the most common
one and is made of cotton or synthetic fibres ( for
low temperatures) or glass cloth fabrics (for higher temperature up to 290oC).
(ii) Electrostatic precipitators (ESP) :
·
The emanating dust is charged with ions and the ionized
particulate matter is collected on an oppositely charged surface.
·
The particles are removed from the collection
surface by occasional shaking or by rapping the surface.
·
ESPs are used in boilers, furnaces, and many
other units of thermal power plants, cement factories, steel plants,
etc.
(iii) Inertial collectors :
·
It works on the
principle that inertia of SPM in a gas is higher than its solvent and as
inertia is a function of the mass of the particulate matter this device
collects heavier particles more efficiently.
·
‘Cyclone’ is a
common inertial collector used in gas cleaning plants.
(iv) Scrubbers :
·
Scrubbers are wet collectors.
·
They remove aerosols from a stream of gas
either by collecting wet particles on a surface followed by their removal, or
else the particles are wetted by a scrubbing liquid.
(iv) Control of vehicular pollution :
·
In cities like Delhi, motor vehicles need to
obtain Pollution Under Control (PUC) certificate at regular intervals.
·
This ensures that levels of pollutants
emitted from vehicle exhaust are not beyond the prescribed legal limits.
·
The price of diesel is much cheaper than
petrol which promotes use of diesel.
·
To reduce emission of
sulphurdioxide, sulphur content in diesel has been reduced to 0.05%.
·
Earlier lead in the form of tetraethyl lead
was added in the petrol to raise octane level for smooth running of engines.
·
Addition of lead in petrol has been banned to
prevent emission of lead particles with the vehicular emission.
OZONE HOLE-CAUSES AND HARM DUE
TO OZONE DEPLETION :
·
The stratosphere
has an ozone layer which protects the earth’s surface from excessive ultraviolet
(UV) radiation from the Sun.
·
Chlorine from chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
used for refrigeration, air conditioning, fire extinguishers, cleaning
solvents, aerosols (spray cans of perfumes, medicine, insecticide) cause damage to ozone layer chlorine contained in the
CFCs on reaching the ozone (O3) layer split the ozone molecules to form oxygen
(O2).
·
Amount of ozone, thus gets reduced and cannot
prevent the entry of UV radiation.
·
There has been a reduction of
ozone umbrella or shield over the Arctic and Antarctic regions. This is known
as ozone hole.
·
This permits passage of UV
radiation on earth’s atmosphere which causes
sunburn, cataract in eyes leading to blindness, skin cancer, reduced
productivity of forests, etc.
·
Under the “Montreal
Protocol” amended in 1990 it was decided to completely phase out CFCs to
prevent damage of ozone layer.
GLOBAL WARMING AND GREENHOUSE
EFFECT :
·
Atmospheric gases like carbondioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons
are capable of trapping the out-going infrared radiation from the earth.
·
Infra-red radiations trapped by the earth’s
surface cannot pass through these gases and to increase thermal energy or heat
in the atmosphere.
·
Thus, the temperature of the global atmosphere
is increased.
·
As this phenomenon of increase in temperature
is observed in green houses, in the botanical gardens these gases are known as
green house gases and the heating effect is known as green house effect.
·
If greenhouse gases are not
checked, by the turn of the century the temperature may rise by 50C.
·
This will melt the polar ice caps and
increase the sea level leading to coastal flooding, loss of coastal areas and
ecosystems like swamps and marshes, etc.
NOISE POLLUTION :
·
Noise is one of the most pervasive pollutant.
A musical clock may be nice to listen during the day, but may be an irritant
during sleep at night.
·
Noise by definition is “sound without value”
or “any noise that is unwanted by the recipient”.
·
Noise in industries such as stone cutting and
crushing, steel forgings , loudspeakers, shouting by hawkers selling their
wares, movement of heavy transport vehicles, railways and airports leads to
irritation and an increased blood pressure, loss of temper, decrease in work
efficiency, loss of hearing which may be first temporary but can become
permanent in the noise stress continues.
·
Noise level is measured in
terms of decibels (dB). W.H.O. (World Health Organization) has prescribed
optimum noise level as 45 dB by day and 35 dB by night. Anything above 80 dB is
hazardous.
Effects of noise pollution :
·
Noise pollution is highly annoying and
irritating.
·
Noise disturbs sleep, causes hypertension (high
blood pressure), emotional problems such as aggression, mental depression and annoyance.
·
Noise pollution adversely affects efficiency and performance of individuals.
WATER POLLUTION :
·
Addition or presence of
undesirable substances in water is called water pollution.
·
Water pollution is one of the most serious
environmental problems.
·
Water pollution is caused by a variety of
human activities such as industrial, agricultural and domestic.
·
Agricultural run off laden with excess
fertilizers and pesticides, industrial effluents with toxic substances and
sewage water with human and animal wastes pollute our water thoroughly.
·
Natural sources of pollution of water are
soil erosion, leaching of minerals from rocks and decaying of organic matter.
·
Rivers, lakes, seas, oceans,
estuaries and ground water sources may be polluted by point or non-point
sources.
·
When pollutants are discharged from a
specific location such as a drain pipe carrying industrial effluents discharged
directly into a water body it represents point source pollution.
·
In contrast non-point sources include discharge of pollutants from diffused sources or from a
larger area such as run off from agricultural fields, grazing lands,
construction sites, abandoned mines and pits, roads and streets.
Pollution due to pesticides and
inorganic chemicals :
·
Pesticides like DDT and others used in
agriculture may contaminate water bodies.
·
Aquatic organisms take up pesticides from
water get into the food chain (aquatic in this case) and move up the food
chain.
·
At higher trophic level they get concentrated
and may reach the upper end of the food chain.
·
Metals like lead, zinc,
arsenic, copper, mercury and cadmium in industrial waste waters adversely
affect humans and other animals.
·
Arsenic pollution of ground water has been
reported from West Bengal, Orissa, Bihar, Western U.P.
·
Consumption of such arsenic polluted water
leads to accumulation of arsenic in the body parts like blood, nails and hairs
causing skin lesions, rough skin, dry and thickening of skin and ultimately skin cancer.
·
Pollution of water bodies by
mercury causes Minamata disease in humans and dropsy in
fishes.
·
Lead causes displexia, cadmium poisoning causes Itai – Itai disease etc.
·
Oil pollution of sea occurs from leakage from
ships, oil tankers, rigs and pipelines.
·
Accidents of oil tankers spill large quantity
of oil in seas which kills marine birds and adversely affects other marine life
and beaches.
(ii) Thermal pollution :
·
Power plants- thermal and nuclear, chemical
and other industries use lot of water (about 30 % of all abstracted water) for
cooling purposes and the used hot water is discharged into rivers, streams or
oceans.
·
The waste heat from the boilers and heating
processes increases the temperature of the cooling water.
·
Discharge of hot water may
increase the temperature of the receiving water by 10 to 15 °C above the
ambient water temperature. This is thermal pollution.
·
Increase in water temperature
decreases dissolved oxygen in water which adversely affects aquatic life.
·
Unlike terrestrial ecosystems, the
temperature of water bodies remain steady and does not change very much.
·
Accordingly, aquatic organisms are adopted to
a uniform steady temperature of environment and any fluctuation in water
temperature severely affects aquatic plants and animals.
·
Hence discharge of hot water from power
plants adversely affects aquatic organisms.
·
Aquatic plants and animals in
the warm tropical water live dangerously close to their upper limit of
temperature, particularly during the warm summer months.
·
It requires only a slight deviation from this
limit to cause a thermal stress to these organisms.
·
Discharge of hot water in water body affects
feeding in fishes, increases their metabolism and affects their growth.
·
Their resistance to diseases and parasites
decreases.
·
Due to thermal pollution biological diversity
is reduced.
·
One of the best methods of reducing thermal
pollution is to store the hot water in cooling ponds, allow the water to cool
before releasing into any receiving water body .
















Accidents of oil tankers spill large quantity of oil in seas which kills marine birds and adversely affects other marine life and beaches.Aluminium Scaffolding Manufacturer
ReplyDeleteHi, i just want to tell everyone out there that i got my loan of $1,000,000.00 from Mr Ben loan investment program and is 100% legit contact via email: 247officedept@gmail.com or Text him on whatsapp + 1-989-394-3740. if you are seeking for 100% financing at the low rate of 2% rate in return.
ReplyDeleteIn Jaipur, several coaching institutes offer quality preparation for the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) exams. Among them, some top-rated options include Career Launcher, Mahendra's Institute, Paramount Coaching Center, and KD Campus. Best SSC Coaching in Jaipur. These institutes provide comprehensive study material, experienced faculty, regular mock tests, and doubt clearing sessions to help students excel in SSC exams. Each institute has its unique teaching methodology and success stories. Prospective SSC exam candidates in Jaipur can research and visit these institutes to find the one that best suits their learning style, budget, and schedule, ensuring effective preparation and success in the competitive exams.
ReplyDeleteIn Jaipur, several coaching institutes offer quality preparation for the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) exams. Among them, some top-rated options include Career Launcher, Mahendra's Institute, Paramount Coaching Center, and KD Campus. Best SSC Coaching in Jaipur. These institutes provide comprehensive study material, experienced faculty, regular mock tests, and doubt clearing sessions to help students excel in SSC exams. Each institute has its unique teaching methodology and success stories. Prospective SSC exam candidates in Jaipur can research and visit these institutes to find the one that best suits their learning style, budget, and schedule, ensuring effective preparation and success in the competitive exams.